An example that uses tkz-2d.
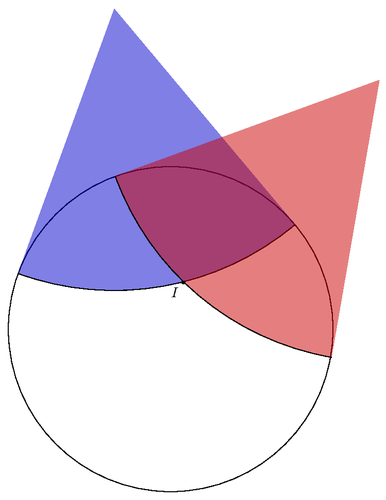
Edit and compile if you like:
% Author: Andrew Mertz
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{tikz,tkz-2d}
\usepackage[graphics,tightpage,active]{preview}
\setlength{\PreviewBorder}{3pt}
\PreviewEnvironment{tikzpicture}
\begin{document}
\begin{tikzpicture}
% Initialize tkz-2d and set the range of x and y values
\tkzInit[xmin=-4.1,xmax=5.2,ymin=-4.1,ymax=8]
\tkzClip
% Define two points using TikZ. Note TikZ coordinates can be given
% in polar form.
\coordinate (A) at (100:8);
\coordinate (B) at (50:8);
% Draw a circle. Note star form of \tkzPoint defines points but does
% not draw them.
\tkzPoint*(0,0){C} % center of circle
\tkzPoint*(0,4){R} % radius of circle
\tkzCircle(C,R)
% Define the points that are tangent to the circle where the tangent
% line passes through either A or B
\tkzTgtFromP(C,C,R)(A){D}{E}
\tkzTgtFromP(C,C,R)(B){F}{G}
% Compute the distance between A and D (the result is stored in
% \tkzmathLen)
\tkzMathLength(A,D)
% Fill and highlight the sector centered at A
\tkzFillSector*[color=blue!80!black,opacity=0.5](A,\tkzmathLen pt)(D,E)
\tkzArc*(A,A,D)(D,E)
% Fill and highlight the sector centered at B
\tkzMathLength(B,F)
\tkzFillSector*[color=red!80!black,opacity=0.5](B,\tkzmathLen pt)(F,G)
\tkzArc*(B,B,F)(F,G)
% Find the intersection of the two arcs
\tkzInterCC(A,A,D)(B,B,F){H}{I}
% Draw the intersection
\tkzDrawPoint[pos=below left](I)
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}
% LocalWords: TikZ tkz xmin xmax ymin ymax LocalWords
Click to download: intersecting-arcs.tex • intersecting-arcs.pdf
Open in Overleaf: intersecting-arcs.tex


