This is a drawing of a tetrahedron inscibed in a parallelepiped. See the following reference p. 58-63 S 189 to 202
@BOOK{altshiller1935modern,
title = {Modern pure solid geometry},
publisher = {The Macmillan company},
year = {1935},
author = {Altshiller-Court, N.},
address = {New York},
edition = {first},
lccn = {35024297},
url = {http://books.google.ca/books?id=DDYGAQAAIAAJ}
}
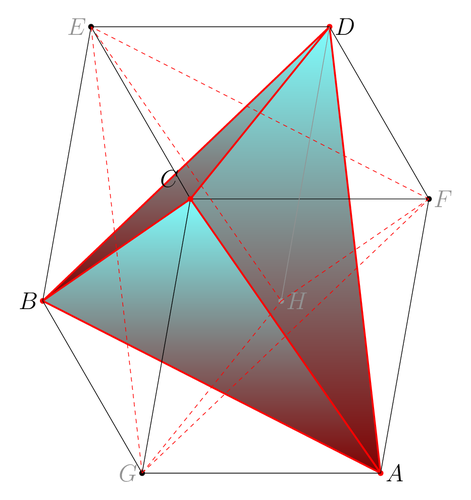
Edit and compile if you like:
% Circumscribed Parallelepiped
% Author: Axel Pavillet
\documentclass[tikz,border=10pt]{standalone}
\begin{document}
\begin{tikzpicture}[font=\LARGE]
% Figure parameters (tta and k needs to have the same sign)
% They can be modified at will
\def \tta{ -10.00000000000000 } % Defines the first angle of perspective
\def \k{ -3.00000000000000 } % Factor for second angle of perspective
\def \l{ 6.00000000000000 } % Defines the width of the parallelepiped
\def \d{ 5.00000000000000 } % Defines the depth of the parallelepiped
\def \h{ 7.00000000000000 } % Defines the heigth of the parallelepiped
% The vertices A,B,C,D define the reference plan (vertical)
\coordinate (A) at (0,0);
\coordinate (B) at ({-\h*sin(\tta)},{\h*cos(\tta)});
\coordinate (C) at ({-\h*sin(\tta)-\d*sin(\k*\tta)},
{\h*cos(\tta)+\d*cos(\k*\tta)});
\coordinate (D) at ({-\d*sin(\k*\tta)},{\d*cos(\k*\tta)});
% The vertices Ap,Bp,Cp,Dp define a plane translated from the
% reference plane by the width of the parallelepiped
\coordinate (Ap) at (\l,0);
\coordinate (Bp) at ({\l-\h*sin(\tta)},{\h*cos(\tta)});
\coordinate (Cp) at ({\l-\h*sin(\tta)-\d*sin(\k*\tta)},
{\h*cos(\tta)+\d*cos(\k*\tta)});
\coordinate (Dp) at ({\l-\d*sin(\k*\tta)},{\d*cos(\k*\tta)});
% Marking the vertices of the tetrahedron (red)
% and of the parallelepiped (black)
\fill[black] (A) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[red] (B) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[black] (C) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[red] (D) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[red] (Ap) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[black] (Bp) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[red] (Cp) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[black] (Dp) circle [radius=2pt];
% painting first the three visible faces of the tetrahedron
\filldraw[draw=red,bottom color=red!50!black, top color=cyan!50]
(B) -- (Cp) -- (D);
\filldraw[draw=red,bottom color=red!50!black, top color=cyan!50]
(B) -- (D) -- (Ap);
\filldraw[draw=red,bottom color=red!50!black, top color=cyan!50]
(B) -- (Cp) -- (Ap);
% Draw the edges of the tetrahedron
\draw[red,-,very thick] (Ap) -- (D)
(Ap) -- (B)
(Ap) -- (Cp)
(B) -- (D)
(Cp) -- (D)
(B) -- (Cp);
% Draw the visible edges of the parallelepiped
\draw [-,thin] (B) -- (A)
(Ap) -- (Bp)
(B) -- (C)
(D) -- (C)
(A) -- (D)
(Ap) -- (A)
(Cp) -- (C)
(Bp) -- (B)
(Bp) -- (Cp);
% Draw the hidden edges of the parallelepiped
\draw [gray,-,thin] (Dp) -- (Cp);
(Dp) -- (D);
(Ap) -- (Dp);
% Name the vertices (the names are not consistent
% with the node name, but it makes the programming easier)
\draw (Ap) node [right] {$A$}
(Bp) node [right, gray] {$F$}
(Cp) node [right] {$D$}
(C) node [left,gray] {$E$}
(D) node [left] {$B$}
(A) node [left,gray] {$G$}
(B) node [above left=+5pt] {$C$}
(Dp) node [right,gray] {$H$};
% Drawing again vertex $C$, node (B) because it disappeared behind the edges.
% Drawing again vertex $H$, node (Dp) because it disappeared behind the edges.
\fill[red] (B) circle [radius=2pt];
\fill[gray] (Dp) circle [radius=2pt];
% From the reference and this example one can easily draw
% the twin tetrahedron jointly to this one.
% Drawing the edges of the twin tetrahedron
% switching the p_s: A <-> Ap, etc...
\draw[red,-,dashed, thin] (A) -- (Dp)
(A) -- (Bp)
(A) -- (C)
(Bp) -- (Dp)
(C) -- (Dp)
(Bp) -- (C);
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}
Click to download: parallelepiped.tex • parallelepiped.pdf
Open in Overleaf: parallelepiped.tex